SQL*Loader
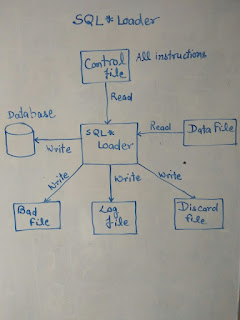
SQL*Loader:-SQL*Loader is an Oracle-supplied utility that allows you to load data from a flat file into one or more database tables.
1) DATA FILE:- This is the input text file that contains the data which needs to be
loaded into an oracle table.
Note:-Data file is optional as we can put data in
control file at last in begin data section
2) CONTROL FILE:- This file written by the programmer to load the data from data file to database table. This file contains the instructions to the sql loader utility. This tells the location of the input file, the format of the input file, and other optional meta data information required by the sql loader .
Note:-We can also define (name and path) of discard
file and bad file here.
3) BAD FILE :- This file is created by SQL*Loader utility and this file has the all rejected records.
Note:-char/varchar data will not be loaded into NUMBER fields, and numbers will not be loaded into DATE fields. Records that doesn't convert to the destination datatype are rejected and written to the bad file. It is created automatically having extension .bad
4) DISCARD FILE :- SQL*Loader allows us to load selective data by WHEN clause. you can specify conditions under which a record will be accepted. Records not meeting those conditions are not loaded in database these records written into the discard file.
It is created automatically having extension .dsc
5) LOG FILE :- It contains status of load process such as number of rows processed and number of rows loaded, number of rows discarded
Data Types for
SQL Loader:- char, decimal external, integer
external
Loading Mode:-
1) Insert :- It works only when target table is empty
2) Append :-It allow to insert data into non-empty table.
3) Replace :- It delete all records first then load the data. The user must have DELETE privilege
4) Truncate:-It truncate table first then load the data and can not
be rolled back.
Option Clause:- bindsize = n
direct
= {TRUE | FALSE}
errors
= n
load = n
multithreading
= {TRUE | FALSE}
parallel
= {TRUE |FALSE}
readsize
= n
resumable
= {TRUE | FALSE}
resumable_name
= 'ant_string'
resumable_timeout
= n
rows
= n
silent
= {HEADER | FEEDBACK | ERRORS | DISCARDS | PARTITIONS | ALL}
skip
= n
skip_index_maintenance
= { TRUE | FALSE}
skip_unusable_indexes
= { TRUE | FALSE}
streamsize
= n
Note:- You can get all options from "help"
command on command prompt
$sqlldr
-help
Syntax of Control File:-
OPTIONS ( ERRORS = n, SILENT = (FEEDBACK))
LOAD DATA
INFILE ''
{INSERT | APPEND | TRUNCATE | REPLACE } into table
field terminated by "," optionally enclosed by " "
WHEN
( position(:)
, position(:) ,...)
Note:- If data file and control file are in same path then no need to mention the path of data file in control file.
Note:- Before going to use SQL*Loader utility , you have ensure that target table is already created in database.
Example1 :- data file for loading in database
$ cat employee.txt
100,Thomas,Sales,5000
200,Jason,Technology,5500
300,Mayla,Technology,7000
400,Nisha,Marketing,9500
500,Randy,Technology,6000
501,Ritu,Accounting,5400
Control File
$ cat example1.ctl
load data
infile '/home/oracle/employee.txt'
insert into table employee
fields terminated by "," optionally enclosed by " "
( id, name, dept, salary )
Note:-Always put data and control file in same path so that no need to mention data file path in control file. if both files are in same path then control file will be as below
$ cat example1.ctl
load data
infile employee.txt
insert into table employee
fields terminated by "," optionally enclosed by " "
( id, name, dept, salary )
The above control file indicates the following:
infile :– Indicates the location of the input data
file
into table :– Indicates the table name where this data
should be inserted
fields terminated by :– Indicates the delimiter that
is used in the input file to separate the fields
optionally enclosed by :-Indicate field data enclosed by that character
optionally enclosed by :-Indicate field data enclosed by that character
( id, name, dept, salary ) :– Lists the name of the
column names in the table into which the data should be uploaded
Firstly need to check that table is available in database or not
SQL>select * from tab where tname='EMPLOYEE';
If table does not exists then create first
SQL> create table employee(id integer,name
varchar2(10),dept varchar2(15),salary integer,hiredon date);
Note: If you don’t have the table created, you’ll get
the following error message:
SQL*Loader-941: Error during describe of table
EMPLOYEE
ORA-04043: object EMPLOYEE does not exist
Move to directory where data file and control file are placed
$cd /home/oracle
Run the following command to load the data
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=example1.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 5
Verify the the records are created in the database
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
-------
100
Thomas Sales 5000
200
Jason Technology 5500
300
Mayla Technology 7000
400
Nisha Marketing 9500
500
Randy Technology 6000
This will create the output log file in the same name
as the data file, but with the .log extension (instead of .ctl). Partial output
shown below.
$ cat sqlldr-add-new.log
Control File:
/home/ratnesh/sqlldr-add-new.ctl
Data File:
/home/ratnesh/employee.txt
Table EMPLOYEE:
5 Rows
successfully loaded.
0 Rows not
loaded due to data errors.
0 Rows not
loaded because all WHEN clauses were failed.
0 Rows not
loaded because all fields were null.
Elapsed time was:
00:00:00.04
CPU time was:
00:00:00.00
2. Inserting Additional Records
Let us say you want to add two new employees to the
employee table from the following newemployee.txt file.
$ vi newemployee.txt
600,Ritu,Accounting,5400
700,Jessica,Marketing,7800
If you create a similar control file like the previous
example, you might get the following error message.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger control=/home/ratnesh/sqlldr-add-more.ctl
SQL*Loader-601: For INSERT option, table must be
empty. Error on table EMPLOYEE
The above indicates that the table should be empty
before you can upload data using sql*loader.
If you like to insert more data to the tables without
having to delete the existing rows, use the “append’ command as shown in the
following control file.
$ vi sqlldr-append-more.ctl
load data
infile newemployee.txt
append into table employee
fields terminated by ","
( id, name, dept, salary )
Now, if you do sqlldr this will append the data.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-append-more.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 2
Verify that the records are appended successfully
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
-------
100
Thomas Sales 5000
200
Jason Technology 5500
300
Mayla Technology 7000
400
Nisha Marketing 9500
500
Randy Technology 6000
600
Ritu Accounting 5400
700
Jessica Marketing 7800
3. Data inside the Control File using BEGINDATA
You can also specify the data directly inside the
control file itself using BEGINDATA keyword. i.e Anything that comes after
BEGINDATA will be treated as data to be uploaded to the table as shown below.
$ cat sqlldr-add-new-with-data.ctl
load data
infile *
append into table employee
fields terminated by ","
( id, name, dept, salary )
begindata
100,Thomas,Sales,5000
200,Jason,Technology,5500
300,Mayla,Technology,7000
400,Nisha,Marketing,9500
500,Randy,Technology,6000
Note: The infile will say ‘*’ in this case, as there
is no input data file name for this example.
Execute sqlldr to upload the data from the control
file.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger control=/home/ratnesh/sqlldr-add-new-with-data.ctl
4. Date format and Different Delimiter
This example shows how to specify a date format in the
control file and how to handle different delimiters in a data file
The following example has different delimiters ($
after name, ^ after department).
$ cat employee-date.txt
100,Thomas$Sales^5000,31-JAN-2008
200,Jason$Technology^5500,01-Feb-2005
300,Mayla$Technology^7000,10-Aug-2000
400,Nisha$Marketing^9500,12-Dec-2011
500,Randy$Technology^6000,01-JAN-2007
Create the following control file and indicate the field
delimiters for each and every field using “terminated by” as shown below.
$cat sqlldr-date.ctl
load data
infile employee-date.txt
truncate into table employee
fields terminated by ","
( id, name terminated by "$", dept
terminated by "^", salary, hiredon DATE "dd-mon-yyyy" )
Load the data using sqlldr as shown below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-date.ctl
Verify that the data got loaded properly as shown
below.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
100
Thomas Sales 5000 31-JAN-08
200
Jason Technology 5500 01-FEB-05
300
Mayla Technology 7000 10-AUG-00
400
Nisha Marketing 9500 12-DEC-11
500
Randy Technology 6000 01-JAN-07
5. Fixed Length Data Upload
If you have a data file without data that are fixed
length (i.e without any delimiter), you can use this example to upload this
data.
For this example, let us use the following file which
has data that are of fixed length. For example, 1st three characters are always
employee number, Next 5 characters are always employee name, etc.
$ cat employee-fixed.txt
200JasonTechnology5500
300MaylaTechnology7000
400NishaTechnology9500
500RandyTechnology6000
Create the following control file, where you specific
the position of each and every field as shown below using the
“Position(start:end)” syntax.
$ cat sqlldr-fixed.ctl
load data
infile employee-fixed.txt
truncate into table employee
fields terminated by "," optionally enclosed by " "
( id position(1:3), name position(4:8), dept
position(9:18), salary position(19:22) )
Load this fixed length data using the sqlldr as shown
below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger control=sqlldr-fixed.ctl
Verify that the data got loaded.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
200
Jason Technology 5500
300
Mayla Technology 7000
400 Nisha Technology 9500
500
Randy Technology 6000
6. Change the data during upload
You can also massage the data and change it during
upload based on certain rules.
In the following control file:
id is incremented by 999 before uploading. i.e if the
emp id is 100 in the data file, it will be loaded as 1099
Convert the name to upper case and load it. This uses
the upper function.
If the department contains the value “Technology”
change it to “Techies”. This uses decode function
$ cat sqlldr-change-data.ctl
load data
infile employee.txt
truncate into table employee
fields terminated by "," optionally enclosed by " "
( id ":id+999",name
"upper(:name)",dept
"decode(:dept,'Technology','Techies', :dept)",salary)
Load the data using this control file which will
massage the data before uploading it.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger control=sqlldr-change-data.ctl
Verify that the data got changed while loading as per
our rules.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
1099
THOMAS Sales 5000
1199
JASON Techies 5500
1299
MAYLA Techies 7000
1399
NISHA Marketing 9500
1499
RANDY Techies 6000
7. Load data from multiple data files
To load data from multiple files, you just have to
specify multiple infile in the control file.
The following control file loads data from two
different data files (employee.txt and newemployee.txt) to the employee table.
$ sqlldr-add-multiple.ctl
load data
infile employee.txt
infile newemployee.txt
append into table
employee
fields terminated
by ","
( id, name,
dept, salary )
Load the data using this control file which will
upload data from multiple data files as shown below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-add-multiple.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 5
Commit point reached - logical record count 7
8. Load data to Multiple Tables
Create another table called bonus which will have
employee id and bonus columns.
SQL>create table bonus( id integer,bonus integer);
Create the employee-bonus.txt data file that contains
the fields: id, name, department, salary, bonus
$ cat employee-bonus.txt
100 Thomas Sales
5000 1000
200 Jason
Technology 5500 2000
300 Mayla
Technology 7000 2000
400 Nisha
Marketing 9500 1000
500 Randy
Technology 6000 3000
Create the control file as shown below, which will
upload the data from the above file to two different tables. As shown below,
you should have two “into table” commands, and specify the position of the data
which needs to be used to upload the data to that column.
$ cat sqlldr-multiple-tables.ctl
load data
infile employee-bonus.txt
truncate into table employee
( id position(1:3),name position(5:10),dept
position(12:21),salary position(23:26))
truncate into table bonus
( id position(1:3),bonus position(28:31))
Load the data to multiple tables using this control
file as shown below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-multiple-tables.ctl
Verify that the data got loaded to multiple tables
successfully.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
100
Thomas Sales 5000
200
Jason Technology 5500
300
Mayla Technology 7000
400
Nisha Marketing 9500
500
Randy Technology 6000
SQL> select * from bonus;
ID BONUS
---------- ----------
100 1000
200 2000
300 2000
400 1000
500 3000
9. Handling Bad (Rejected) Records
In the following example, we have two bad records.
Employee id 300 and 500 has salary column which is not numeric.
$ cat employee-bad.txt
100,Thomas,Sales,5000
200,Jason,Technology,5500
300,Mayla,Technology,7K
400,Nisha,Marketing,9500
500,Randy,Technology,6K
Use the following control file for this example.
$ cat sqlldr-bad.ctl
load data
infile employee-bad.txt
truncate into table employee
fields terminated by ","
( id, name, dept, salary )
Load the data (including the invalid records) using
this control file as shown below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-bad.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 5
As you see from the above output, it still says “logical
record count 5?, but you should check the log files to see if it has rejected
any records.
The log file indicates that 2 records are rejected as
shown below:
Control File: sqlldr-bad.ctl
Data File: employee-bad.txt
Bad File: employee-bad.bad
Discard File:
none specified
Table EMPLOYEE:
3 Rows
successfully loaded.
2 Rows not
loaded due to data errors.
By default the rejected records are stored in a file
that has the same name as the data file (but with .bad extension)
$ cat employee-bad.bad
300,Mayla,Technology,7K
500,Randy,Technology,6K
As you see below, the employee table has only 3
records (as 2 of them were rejected).
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
100
Thomas Sales 5000
200
Jason Technology 5500
400
Nisha Marketing 9500
10. Load Specific Rows from a datafile
If you want to load only a specific records from a
data file use the WHEN in the control file.
Add the line “when” next to “into table” line. In the
following control file, the when clause indicates that it will load only the
records that have dept as “Technology”.
$ cat sqlldr-when.ctl
load data
infile employee.txt
truncate into table employee
when dept = 'Technology'
fields terminated by ","
( id, name, dept, salary )
Load the selective data (only the “Technology”
records) using this control file as shown below.
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=sqlldr-when.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 5
As you see from the above output, it still says
“logical record count 5?, but you should check the log files to see how many
records were loaded, and how many records were discarded because it didn’t
match the when condition.
The following from the log file shows that 5 records
were read, and 2 of them were discarded as it didn’t match the when condition.
Discard File: none
specified
Total logical records read: 5
Total logical records discarded: 2
Verify that only the selective records were loaded
into the table.
SQL> select * from employee;
ID
NAME DEPT SALARY HIREDON
---------- ---------- --------------- ----------
---------
200
Jason Technology 5500
300
Mayla Technology 7000
500
Randy Technology 6000
Dealing with null values in datafile
$ cat employee_rec.txt
1, Amit, msc, jalandhar, 1-12-1980
2,ajay, bca, banga
3,akshay, bsc, jalandhar
4,jatinder, msc
5, arun, msc, jalandhar, 25-12-1982
Use the following control file for this example.
$cat employee_rec_load.ctl
load data
infile employee.txt
truncate into table student
fields terminated by ',‘
TRAILING NULLCOLS
(rollno,name,course,address,dob date
"dd-mm-yyyy")
Create another table called student which will have
rollno,name,course,address and dob columns.
SQL>create table student( rollno number,name
varchar2(20),course varchar2(20),address varchar2(50),dob date);
$ sqlldr scott/tiger
control=employee_rec_load.ctl
Commit point reached - logical record count 5
No comments:
Post a Comment