Exception
Types of exception:-Exceptions are divided below category
1) System defined Exception
a) Named Exception
b) Un-Named Exception
2) User defined Exception
1) System defined (Named Exception):- These are Oracle defined exceptions, There are about 21 predefined exception, these are
1) ACCESS_INTO_NULL ORA-06530
2) CASE_NOT_FOUND ORA-06592
3) COLLECTION_IS_NULL ORA-06531
4) CURSOR_ALREADY_OPEN ORA-06511
5) DUP_VAL_ON_INDEX ORA-00001
6) INVALID_CURSOR ORA-01001
7) INVALID_NUMBER ORA-01722
8) LOGIN_DENIED ORA-01017
9) NO_DATA_FOUND ORA-01403
10) NOT_LOGGED_ON ORA-01012
11) PROGRAM_ERROR ORA-06501
12) ROWTYPE_MISMATCH ORA-06504
13) SELF_IS_NULL ORA-30625
14) STORAGE_ERROR ORA-06500
15) SUBSCRIPT_BEYOND_COUNT ORA-06533
16) SUBSCRIPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT ORA-06532
17) SYS_INVALID_ROWID ORA-01410
18) TIMEOUT_ON_RESOURCE ORA-00051
19) TOO_MANY_ROWS ORA-01422
20) VALUE_ERROR ORA-06502
21) ZERO_DIVIDE ORA-01476
Examples:-
No_data_found :- This Exception is used to handle the program when query return no row.
Example 1:- Write a program to handle the Exception "no_data_found"
SQL>declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where empno=&empno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-01403: no data found
ORA-06512: at line 4
To handle this error we use exception "no_data_found" . Below is the example for same
SQL>declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where empno=&empno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
exception
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('No such employee exist');
end;
/
Too_many_rows:- This Exception is used to handle the program when query return more than one row
Example2:-Write a program to handle the Exception "Too_many_rows"
SQL>declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where deptno=&deptno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-01422: exact fetch returns more than requested number of rows
ORA-06512: at line 4
To handle this error we can use "too_many_rows" Exception. Below is the example for same
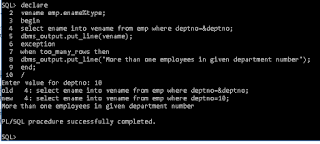
declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where deptno=&deptno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
exception
when too_many_rows then
dbms_output.put_line('More than one employees in given department number');
end;
/
Example3:-Write a program to handle the exception "no_data_found" and "too_many_rows"
SQL>declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where deptno=&deptno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
exception
when too_many_rows then
dbms_output.put_line('More than one employees in given department number');
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('No employees exist in given department number');
end;
/
declare
vename emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into vename from emp where deptno=&deptno;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
exception
when too_many_rows then
dbms_output.put_line('More than one employees in given department number');
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('No employees exist in given department number');
when others then
dbms_output.put_line('unknown error');
end;
/
Invalid_cursor:- This Exception is used to handle the cursor scope
Example5:-Write a program to handle the Exception "Invalid_cursor"
SQL>declare
cursor c1 is select sal from emp;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
loop
fetch c1 into vsal;
exit when c1%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line('Processed records:-'||c1%rowcount);
close c1;
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-01001: invalid cursor
ORA-06512: at line 6
declare
cursor c1 is select sal from emp;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
loop
fetch c1 into vsal;
exit when c1%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line('Processed records:-'||c1%rowcount);
close c1;
exception
when invalid_cursor then
dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is not handled properly');
end;
/
"cursor_already_open" Exception:-
declare
cursor c1 is select sal from emp;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
open c1;
loop
open c1;
fetch c1 into vsal;
exit when c1%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line('Processed records:-'||c1%rowcount);
close c1;
exception
when invalid_cursor then
dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is not handled properly');
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-06511: PL/SQL: cursor already open
ORA-06512: at line 2
ORA-06512: at line 7
declare
cursor c1 is select sal from emp;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
open c1;
loop
open c1;
fetch c1 into vsal;
exit when c1%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line('Processed records:-'||c1%rowcount);
close c1;
exception
when cursor_already_open then
dbms_output.put_line('You are trying to open cursor which is already open');
end;
/
"invalid number" Exception:-
create table abc(name varchar2(10),sal number);
begin
insert into abc values('ABC','100');
end;
/
begin
insert into abc values('XYZ','xyz');
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-01722: invalid number
ORA-06512: at line 2
begin
insert into abc values('XYZ','xyz');
exception
when invalid_number then
dbms_output.put_line('You are using invaid datatyes');
end;
/
"value error" Exception :-
declare
tot number;
begin
tot:='&a'+'&b';
dbms_output.put_line(tot);
end;
/
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-06502: PL/SQL: numeric or value error: character to number conversion error
ORA-06512: at line 4
declare
tot number;
begin
tot:='&a'+'&b';
dbms_output.put_line(tot);
exception
when value_error then
dbms_output.put_line('please use correct data' );
end;
/
User defined exception:- We can declare our own exception and can raise in anywhere in program.When user defined exception raised then exception block called to see the definition of that exception.
declare
a exception;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
select sal into vsal from emp where empno=&empno;
if vsal>3000 then
raise a;
else
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end if;
exception
when a then
dbms_output.put_line('Salary is too high');
end;
/
declare
a1 exception;
a2 exception;
a3 exception;
a4 exception;
begin
begin
raise a1;
exception
when a1 then
dbms_output.put_line('Exception a1 handled');
raise a3;
end;
exception
when a2 then
dbms_output.put_line('Exception a2 handled');
when a3 then
dbms_output.put_line('Exception a3 handled');
when a4 then
dbms_output.put_line('Exception a4 handled');
end;
/
Error Trapping Functions:-
1) SQL Code:- It returns number
2) SQL Errm:- It return Error message
declare
name emp.ename%type;
begin
select ename into name from emp where empno=&eno;
exception
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('SQLCODE: '|| SQLCODE);
dbms_output.put_line('SQLERRM: '|| SQLERRM);
end;
/
declare
vsal emp.sal%type;
str varchar2(500);
str1 varchar2(100);
begin
select sal into vsal from emp where empno=&eno;
exception
when others then
str:=sqlerrm;
str1:=sqlcode;
dbms_output.put_line(str);
dbms_output.put_line(str1);
end;
/
declare
cursor c1 is select ename from emp;
vename emp.ename%type;
n number;
begin
open c1;
loop
fetch c1 into vename;
dbms_output.put_line(vename);
exit when c1%notfound;
end loop;
close c1;
n:=c1%rowcount;
exception
when invalid_cursor then
dbms_output.put_line('SQLCODE: '|| SQLCODE);
dbms_output.put_line('SQLERRM: '|| SQLERRM);
end;
/
Raise Application Error :- If you want to display your own user defined
exception code and exception message then we can use raise_application_error
procedure
Syntax:- raise_application_error(error_number,error_message);
error_number:- it should be between -20000 and -20999
error_message :-It should upto maximum 512 characters
declare
a exception;
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
select sal into vsal from emp where empno=&empno;
if vsal>3000 then
raise a;
else
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end if;
exception
when a then
raise_application_error(-20102,'Salary is too high');
end;
/
declare
vsal emp.sal%type;
begin
select sal into vsal from emp where empno=&empno;
if vsal>3000 then
raise_application_error(-20102,'Salary is too high');
else
dbms_output.put_line(vsal);
end if;
end;
/
Practice Question :-
Q1 :- What is Exception in Oracle ?
Q2 :- What are Exception types in Oracle ?



No comments:
Post a Comment